Automation Decision Service¶
Info
Updated 11/19/21
Automation Decision Services provides decision modeling capabilities that help business experts capture and automate repeatable decisions. Automation Decision Services comes with two main components that can be installed separately:
Concepts¶
- Decision Designer to develop decision model. It is connected to Github to manage decision artifacts. It is used to build and deploy the decision runtime.
- Decision Service: runtime to get ruleset and executes rule engine
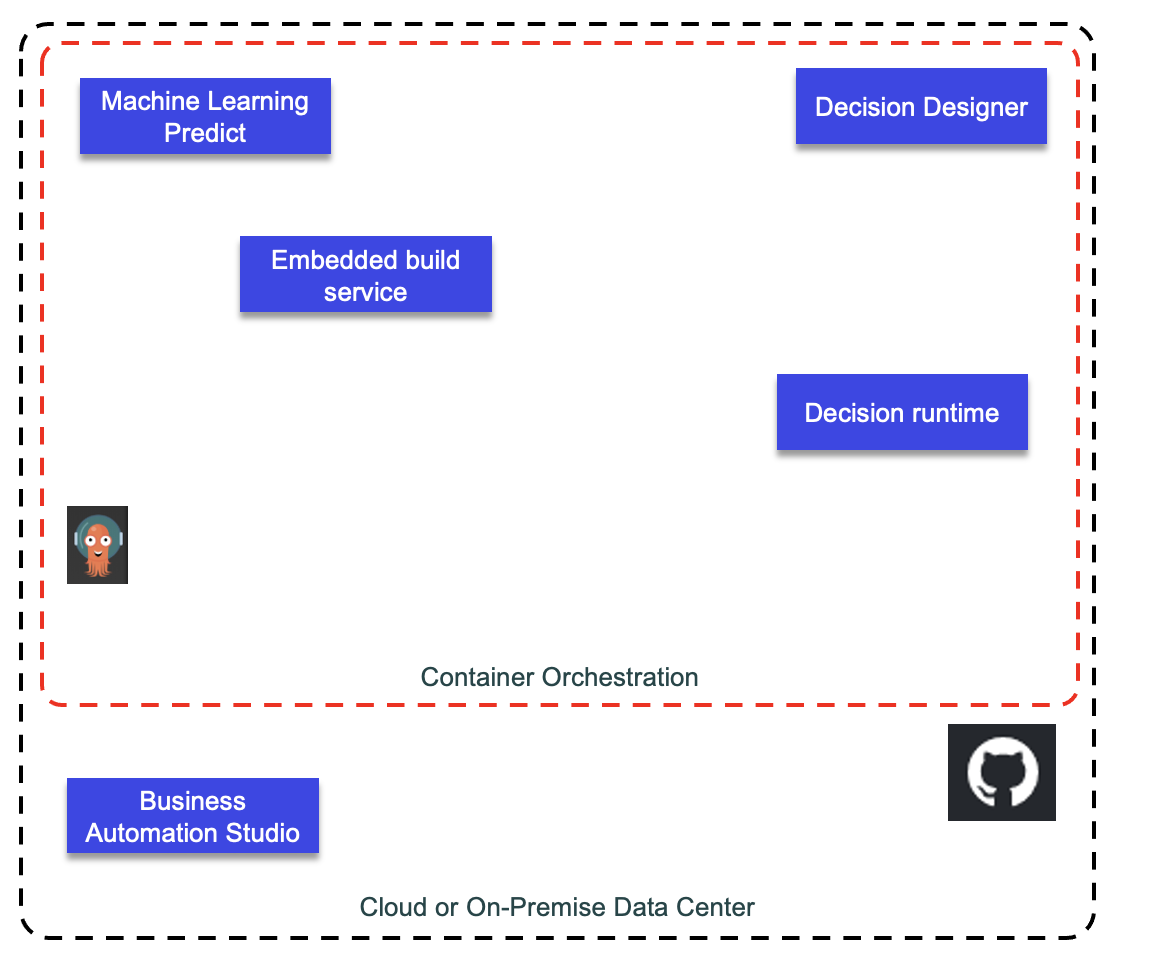
A decision service uses decision artifacts to define a business decision:
- decision model
- data model
- predictive scoring
- external libraries
- decision operations
The decision model may include call to a predictive scoring done with ML model.
Decision model¶
Decision model diagrams are composed of a set of nodes that are used as building blocks to represent decisions in a graphical way:
- Decision nodes represent the end decision, that is the decision that you want to automate, and the subdecisions that the end decision depends on.
- Data nodes represent the data definition that is needed to make a decision.
- Function nodes encapsulate computations from other decision models.
- Prediction nodes encapsulate predictions that you can call directly from your decision model.
- External libraries contain data types and functions to be used inside the decision models
Installation¶
Being part of Cloud Pak for Automation, we need to install it on OpenShift. The install doc is here. Installation uses operator lifecycle manager (OLM).
IBM Cloud Pak for Business Automation comes with the IBM Cloud® platform automation foundation which includes:
- Process Mining from myInvenio
- Robotic Process Automation
- MongoDB
- Zen User Interface
- Biz Automation Insight Apicurio Registry, Kafka, Flink, Elastic Search is now part of Automation Foundation
- Common services: IAM, certificate management, User Management Services, Admin UI, license operator
Summary of installation steps:
- Get IBM license entitled registry key
- Get the storage class name to use for dynamic storage
- Prepare storage for cloud pak operator
- Download the k8s certificates and configuration to prepare the OCP cluster
- Define a project where the Cloud Pak will be installed and then modify the cluster_role_binding
- Run the
cert-kubernetes/descriptors/cp4a-clusteradmin-setup.shscript - Define the custom resource manifest to control the product to install, use create or
oc create -f ... - After the Automation Decision Services container is deployed to the cluster, we need to take additional steps (add maven plugin) to be able to build and deploy decision services.
Getting started¶
Get access to a CP4Automation console, use to the Business Automation Studio.
Got to Design, and click Business automation > Decision > Create and select Decision automation
- Once project is created, need to add a decision service
Data enters through input data nodes, and is processed by rules in decision nodes. The rules define the logic of the decision. They are expressed in business rules and decision tables
- create a decision model using DMNotation
- Add data model to define input and output types
- Add rules and decision tables to the different decision nodes. Combine node output to input to chain decisions.
- Define an operation used to call the service.
- Connect to github repository (first time the repository needs to be empty)
- Deploy to a run time server
- Get the service end point URL. Which is based on a schema like
/deploymentSpaces/{deploymentSpaceId}/decisions/{decisionId}/operations/{operation}/execute/
The deploymentSpaceId is embedded, the decisionId is coming from the deployment, it has a jar name inside, and the operation is the name of the decision service operation selected.
The root URL is the ads-runtime which we can get from
ADS-runtime-access-info:
----
Runtime URL: https://ads-runtime-ibm-cloudpaks.....-0000.us-east.containers.appdomain.cloud/ads/runtime/api/swagger-ui
username: drs
password: .....
The route is using the icp4adeploy-ads-runtime-service service, so if we deploy an app on the same cluster we should be able to get the internal URL.
- Use the integrated swagger-ui to test the service. Use the Authorize to define the user to use to connect. This is the
drsservice user and the password is used.
See this article with screen shots for a bigger example with predictive scoring
Client app¶
A decision runtime instance is deployed as a Kubernetes pod that is based on WebSphere® Application Server Liberty. The runtime archive repository can be any HTTP-based server that is able to store files. The runtime downloads decision service archives from the runtime archive repository. ach decision runtime instance is able to execute multiple distinct decisions. The runtime caches decisions to lower the cost of loading the decision service archives. The decisionId is used as key for rule archive in the cache.
Your client application calls a decision service through the decision runtime REST API.
Collaborating¶
To be able to support CI/CD we need to get the ADS Maven plugin. This is done by performing the ADS post installation tasks:
- Get a UMS user
- Be sure to have installed a Nexus server to OpenShift
- Authenticate to ADS_BASE_URL with the access token of the UMS user.
Not yet there¶
Useful links¶
- Product doc - getting started goes over a simple decision model to send a message according to some weather data.
- ODM Docker image
- ADS Compose
- Eclipse Oxygen needed for Decision Designer
- ADS samples repository
Older info¶
Launch locally ODM for older rule implementation.
docker run -e LICENSE=accept -p 9060:9060 -p 9443:9443 -m 2048M --memory-reservation 2048M -v $PWD:/config/dbdata/ -e SAMPLE=true ibmcom/odm:8.10