Kafka Connect¶
Kafka connect is an open source framework for easily integrate external systems with Kafka. It works with any Kafka products. It uses the concepts of source and sink connectors to ingest or deliver data to / from Kafka topics.
A source connector collects data from a system. A sink connector delivers data from Kafka topics into other systems.
Here is the basic concepts of Kafka Connect integration with Kafka Cluster and external systems

The general concepts are detailed in the Robin Moffatt's video. Here is a quick summary:
- Connector represents a logical job to move data from / to Kafka to / from external systems. Apache Camel offers open source Kafka connectors, or we can implement our own.
- Workers are JVMs running the connectors. For production deployment workers run in cluster or "distributed mode", and leverage the Kafka consumer group management protocol to scale tasks horizontally.
- Tasks: each worker coordinates a set of tasks to move the data. In distributed mode, task states are saved in Kafka topics. They can be started, stopped at any time to support resilience, and scalable data pipeline.
- REST API to configure the connectors and monitors the tasks.
It supports distributed or standalone deployment modes. Fully integrated with Kafka Cluster to keep its states, it automatically manage offset, and handle the complex process of offset commitment.
The following figure illustrates a classical 'distributed' deployment of a Kafka Connect cluster.
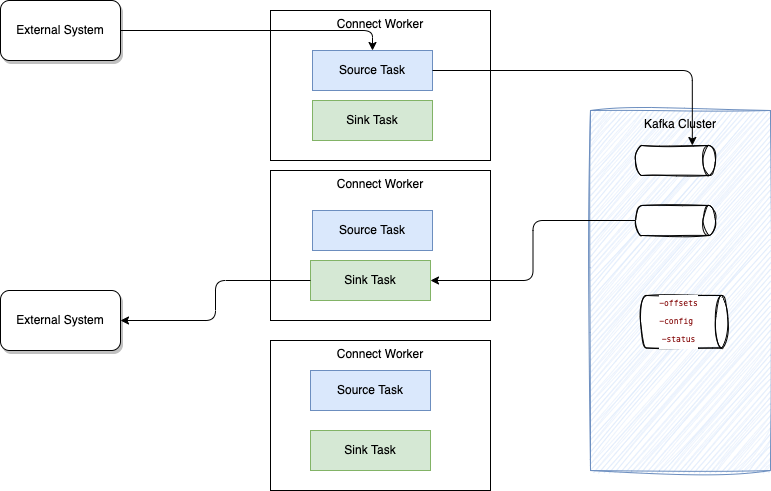
Workers are the running processes (JVMs) to execute connectors and tasks. It uses the existing Kafka group management protocol to scale the worker easily. Each Connector is responsible for defining and updating a set of Tasks that actually move the data. Tasks are threads in a JVM. When a connector is first submitted to the cluster, the workers rebalance the full set of connectors in the cluster with their tasks so that each worker has approximately the same amount of work.
- Connector and tasks are not guaranteed to run on the same instance in the cluster, especially if we have multiple tasks and multiple instances in our Kafka Connect cluster.
- The connector may be configured to add
Converters(code used to translate data between Connect and the system sending or receiving the data), andTransforms: simple logic to alter each message produced by or sent to a connector.
For fault tolerance and offset management, Kafka Connect uses Kafka three topics to persist its states, which may be created when the connectors start are:
- connect-configs: This topic stores the connector and task configurations.
- connect-offsets: This topic stores offsets for Kafka Connect.
- connect-status: This topic stores status updates of connectors and tasks.
Characteristics¶
- Kafka Connect connector, copy a vast quantity of data from source to Kafka: work at the datasource level using native protocol: when the source is a database, it uses JDBC API for example.
- Support streaming and batching.
- Scale from standalone, mono connector to start small, to run tasks in parallel on distributed cluster.
- Kafka Connect defines three models: data model, worker model and connector model. Worker model allows Kafka Connect to scale the application.
- Kafka Connect cluster can serve multiple applications and so may be organized as a service.
- A REST api exists to submit and manage connectors.
Connector cluster configuration¶
The following configurations are important to review:
group.id: one per connect cluster. It is used by source connectors only.heartbeat.interval.ms: The expected time between heartbeats to the group coordinator when using Kafka’s group management facilities.
Fault tolerance¶
When a worker fails:
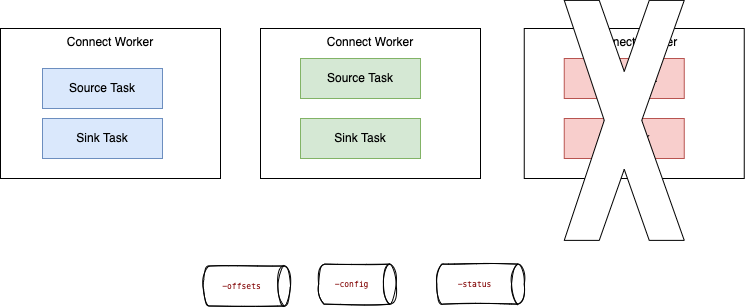
Tasks allocated in the failed worker are reallocated to existing workers, and the task's state, read offsets, source record mapping to offset are reloaded from the different topics.

Installation¶
The Kafka connect framework fits well into a kubernetes deployment. As of now, we have different options for that deployment: the Strimzi Kafka connect operator, install in a VM like an EC2 instances, or use serverless using AWS MSK Kafka Connector.
Local demonstration¶
This lab present the simplest way to demontrate Kafka Connect using File Source and File Sink on a local laptop. The approach is based on docker compose, 1 Kafka broker, 1 topic, and a container running the file connectors in standalone mode or in distributed mode with this sample.
Strimzi¶
KafkaConnector resources allow us to create and manage connector instances for Kafka Connect in a Kubernetes-native way. To manage connectors, we can use the Kafka Connect REST API, or use KafkaConnector custom kubernetes resources. In case of GitOps methodology we will define connector cluster and connector instance as yamls. Connector configuration is passed to Kafka Connect as part of an HTTP request and stored within Kafka itself.
IBM MQ connector¶
The source code is in this repo and uses JMS as protocol to integrate with IBM MQ. When the connector encounters a message that it cannot process, it stops rather than throwing the message away. The MQ source connector does not currently make much use of message keys. It is possible to use CorrelationID as a key by defining MQ source mq.record.builder.key.header property:
key.converter: org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter
value.converter: org.apache.kafka.connect.converters.ByteArrayConverter
mq.record.builder: com.ibm.eventstreams.connect.mqsource.builders.DefaultRecordBuilder
mq.connection.mode: client
mq.message.body.jms: true
mq.record.builder.key.header: JMSCorrelationID
The record builder helps to transform the input message to a Kafka record, using or not a schema.
Always keep the coherence between body.jms, record builder and data converter.
The MQ source task starts a unique JMS Reader that will read n messages from the queue. The `poll() function returns the list of MQ source records, and will commit to JMS if the number of message read match the batch size or if there is no more records. Once the Kafka Producer gets acknowledge that records are received by Brokers then use callback on the source task to commit MQ transaction for example.
Any producer configuration can be modified in the source connector configuration:
producer.override.acks: 1
Example of Kafka Connect Deployments¶
TBD
- File sink and sources in distributed mode sample
- S3 Sink connector
- Kinesis data stream with source connector.