SQL basics¶
In the SQL language we can differentiate the Data Definition Language (DDL), which are statements to create, change, or deleting tables, from Data Modification Language (DML), which are used to define statements to modify the data and to do not change the metadata.
The figure below illustrates some common basic patterns.
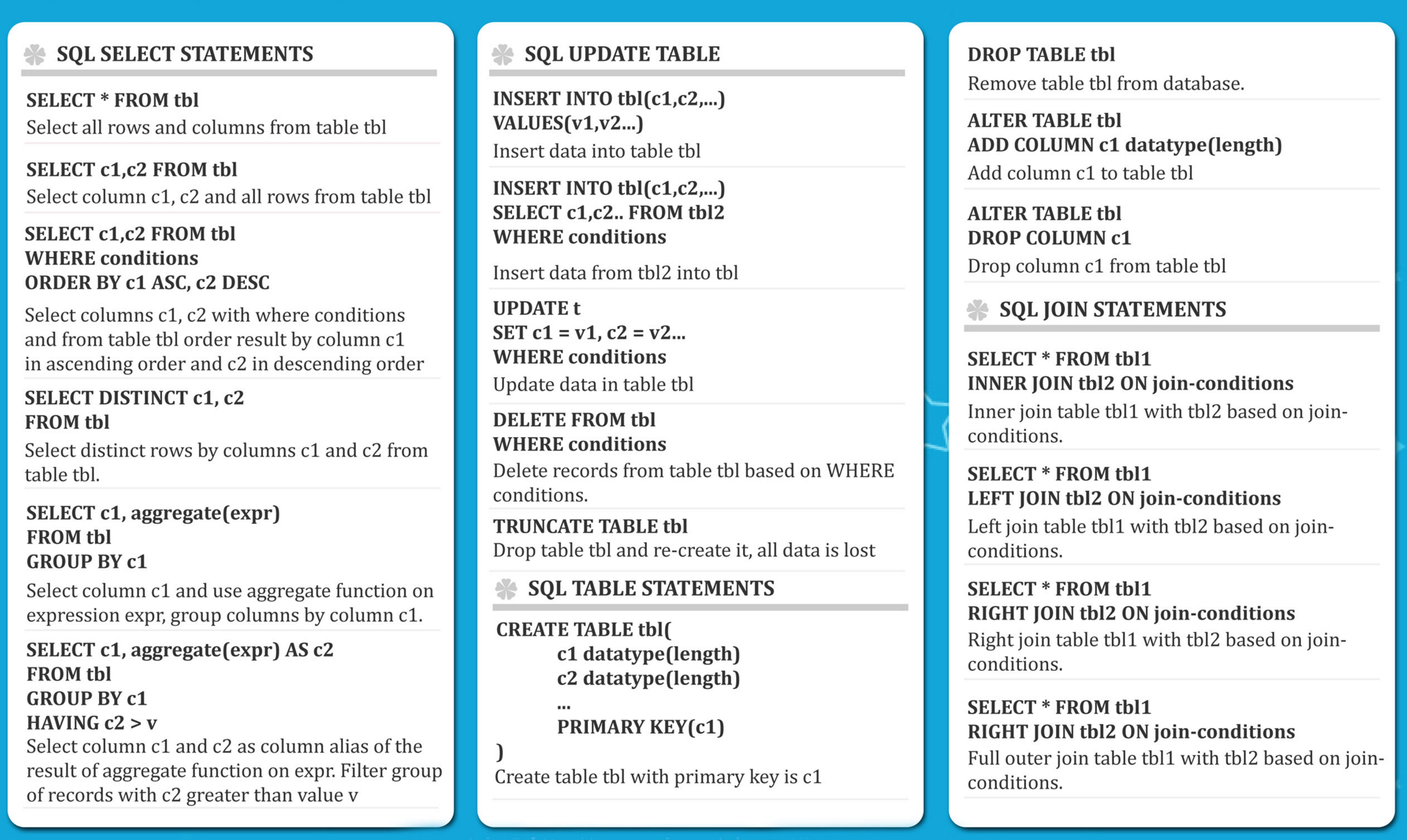
For deeper tutorial see the sqltutorial.org site. The Employee DDL is in DDL folder.
Starting SQL editor¶
As a main playground, I use Postgresql. See setup section to run it with docker or kubernetes. The URL should be http://localhost:5050 user admin@example.com
- Register a server by using the name of the rw service as hostname (pg-cluster-rw) user app, and see the secret for the password.
- Use the
Query Toolto execute SQL command.
Simple getting started¶
Exercises from medium articles¶
-
The SQL Questions with Detailed Answers (Step-by-Step), see the sql scripts in the code/postgresql/medium1 folder.
-
Start docker compose as it mount the
./medium1folder into/tmp/scripts. - Create the tables in the postgres db
- insert records
psql -U postgres -f inser-record-1.sql - Write an SQL query to report all customers who never order anything. Use left join to take all the values from the left table and the common rows from the right table. The left join was performed on the Customer table because we want all the Customers with their Orders.
select * from customers left join orders on customers.id = orders.customer_id;
id | name | id | customer_id
----+-------+----+-------------
3 | Sam | 1 | 3
1 | Joe | 2 | 1
2 | Henry | |
4 | Max | |
select name from customers left join orders on customers.id = orders.customer_id where orders.customer_id is null;
Create customers¶
Here is the complete SQL you can run in psql
CREATE TABLE customers (customer_id varchar(8) PRIMARY KEY, lastname varchar(40) NOT NULL, firstname varchar(40) NOT NULL, zipcode varchar(5), country varchar(40), status integer);
INSERT INTO customers (customer_id,lastname,firstname,zipcode,country,status) VALUES
('C01','Builder','Bob','95050','USA',1),
('C02','Destroyer','Bill','95050','USA',1),
('C03','Climber','Jack','95052','USA',1),
('C04','Messenger','John','95052','USA',1);
or use the command
psql postgres://$POSTGRES_USER:$POSTGRES_PWD@$POSTGRES_HOST/$POSTGRES_DB -a -f /home/dll/customer.sql
Create products¶
Products define fresh product with controlled temperature and humidity to control for the travel.
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id varchar(64) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
description varchar(100),
target_temperature REAL,
target_humidity_level REAL,
content_type integrer
);
INSERT INTO products(product_id,description,target_temperature,target_humidity_level,content_type) VALUES
('P01','Carrots',4,0.4,1),
('P02','Banana',6,0.6,2),
('P03','Salad',4,0.4,1),
('P04','Avocado',6,0.4,1),
('P05','Tomato',4,0.4,2);
psql postgres://$POSTGRES_USER:$POSTGRES_PWD@$POSTGRES_HOST/$POSTGRES_DB -a -f /home/dll/product.sql
Table creation¶
For primary key try to using numerical type and Postgresl sequence like:
Use CHECK to put constraint on column and between column
Alter table¶
Alter table in postgresql - doc
Basic command on a customers table¶
select * from customers;
select distinct(name) from customers;
select count(distinct(rate)) from films;
-- how many customer has the name bob and are older than 18
select count(*) from customer where name = 'bob' and age >= 18;
-- sort by salary
select name, salary from customers order by salary DESC;
-- limit the number of records returned
SELECT name, salary FROM customers ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 10;
-- BETWEEN
select count(*) from payment where amount between 8 and 9;
select * from payment where payment_date between '2007-02-01' and '2007-2-15';
-- IN to test value in a list of options
select count(*) from payment where amount in(0.99, 1.98, 1.99);
-- LIKE and ILIKE (case non-sensitive) to do pattern matching on string
select * from customer where first_name ilike 'J%';
-- Modify the table
alter table customers add column email varchar(100);
-- update a unique record
update customers set email='max@email.com' where id = 4;
-- Aggregate min, max, avg, count,...
select round(avg(replacement_code),3) from film;
-- GROUP BY combined with aggregate. Who is the customer spending the most
select customer_id, sum(amount) from payment group by customer_id order by sum(amount) DESC;
-- get the day with the most transactions
select DATE(payment_date), sum(amount) from payment group by DATE(payment_date) order by sum(amount) DESC;
-- HAVING to allow us to use the aggregate result to filter the result along with group by
select customer_id, sum(amount) from payment
where staff_id = 2
group by customer_id having sum(amount) >= 110;
See also the postgres study for information to run SQL on a local postgresql started with docker compose or kubernetes.
Exercises on the dvdrental database¶
See postgres to restore the database schema and data from the tar file.
-
How many payment transactions were greater than $5.00?
-
How many actors have a first name that starts with the letter P?
* How many unique districts are our customers from? -
How many films have a rating of R and a replacement cost between $5 and $15?
-
How many films have the word Truman somewhere in the title?
-
Which staff member processes the biggest number of transactions?
-
What is the avg replacement cost per film rating?
-
Customer eligible for platinum status having more than 40 transactions
-
Customer who spent more than 100$ with a given staff