ArgoCD tutorial¶
To implement GitOps workflow, we used Argo CD, the GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes which also names OpenShift Gitops on OpenShift. Argo CD models a collection of applications as a project and uses a Git repository to store the application's desired state (a gitops repo). Argo CD compares the actual state of the application in the cluster with the desired state defined in Git and determines if they are out of sync. When it detects the environment is out of sync, Argo CD can be configured to either send out a notification to kick off a separate reconciliation process or Argo CD can automatically synchronize the environments to ensure they match.
ArgoCD is deployed with OpenShift GitOps operator.
If you go to the Developer's Perspective, you can see a topology like:
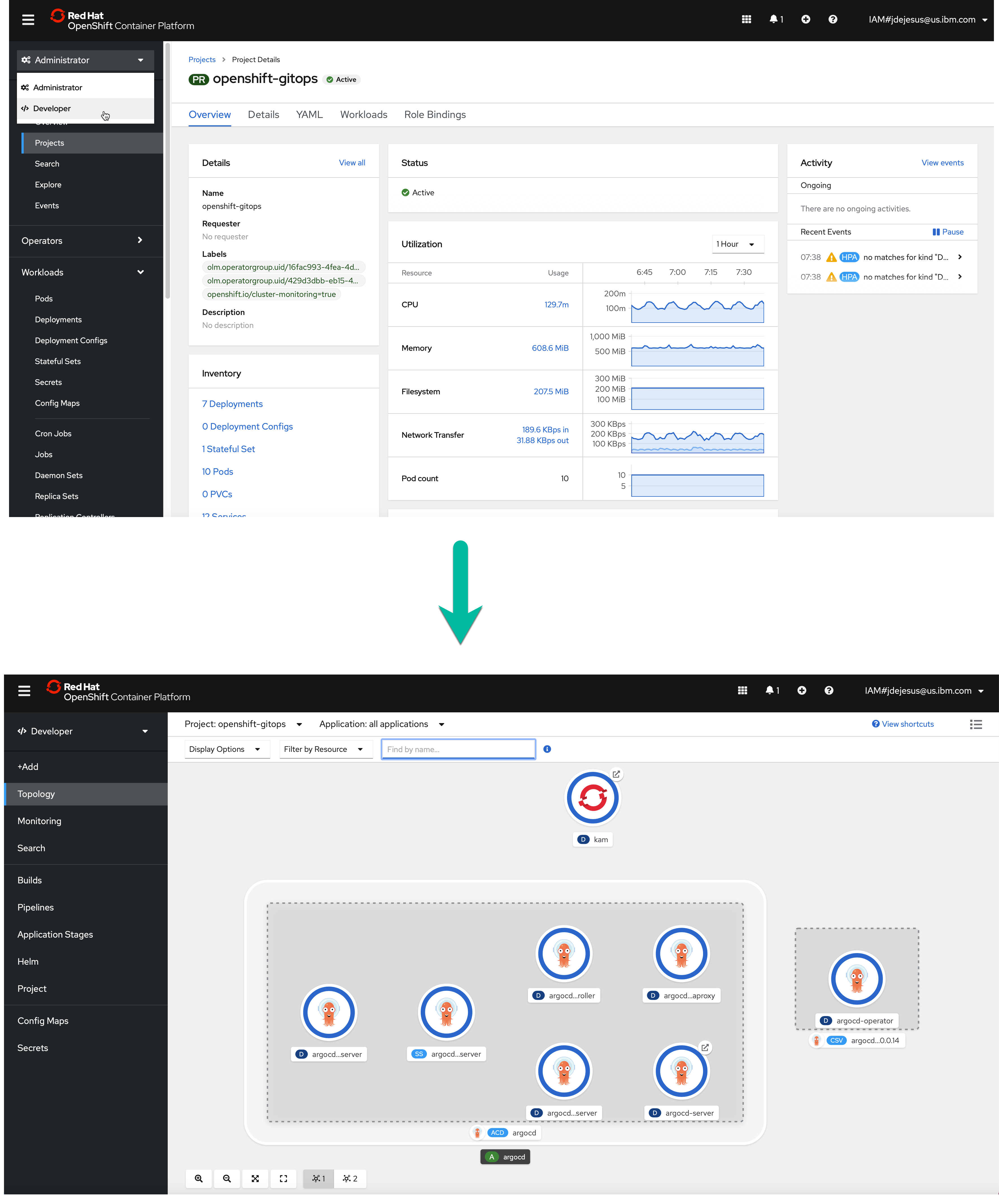
Clicking the Argo Server node that contains the URL takes you to the Argo login page.
See this getting started tutorial and the core concepts.
Installation¶
Installing ArgoCD will include CRD, service account, RBAC policies, config maps, secret and will deploy Redis and argocd server. It makes sense to have one ArgoCD operator deployed per cluster. It can manage projects and within project, applications.
The better approach for installation is to use the Red Hat OpenShift GitOps operator.
# Example of operator installation from https://github.com/jbcodeforce/eda-gitops-catalog
oc apply -k openshift-gitops/operator/overlays/stable
After installing the OpenShift GitOps operator, an instance of Argo CD Operator is installed in the openshift-gitops namespace which has all needed privileges to manage cluster configurations and application deployments. The following pods run:
argocd-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 20h
argocd-dex-server-9dc558f5-4dw4q 1/1 Running 2 20h
argocd-redis-759b6bc7f4-g2jbj 1/1 Running 0 20h
argocd-repo-server-5fbf484547-6x4rj 1/1 Running 0 20h
argocd-server-6d4678f7f6-vqs64
Argo CD console¶
To get the admin user's password, get it from the secret
A route is created to the ArgoCD server:
Within the console we can create application, referencing git repositories, and to kubernetes clusters.
Prepare an application¶
In Argo CD terms, each deployable component is an application and applications are grouped into projects. Projects are not required for ArgoCD to be able to deploy applications, but it helps to organize applications and provide some restrictions on what can be done for applications that make up a project
One ArgoCD server can deploy applications to multiple k8s clusters.
Deploy from the UI¶
Follow the Getting started tutorial, but basically the idea is to define an application, that gets information from git repository to deploy something to k8s as manifests. The configuration specifies what to monitor from the Git and where to deploy the "thing".
The thing will be a kustomization to specify an application deployment.yaml, services, configmap... (It can also use an Helm chart and values files).
Deploy using argocd CLI¶
- Install argocd CLI
On MAC: brew install argocd
- If ArgoCD was installed manually, expose the API server: by default, the Argo CD API server is not exposed with an external IP. Update the service to use load balancer:
Get the IP address of the argocd server: oc get svc then look at the LoadBalancer service (argocd-server) external-IP.
argocd login SERVERIP then use admin user and password. You can also access the ArgoCD UI using the load balancer IP address, admin user and password.
- Define application: this is the deployable unit, which is map to a k8s deployment that references the image built during the CI pipeline. Each component, microservice or app is defined inits own folder and can use Helm or Kustomize to define the deployment, service, configmap...
You use one ArgoCD application per target environment.
Deploy from Yaml¶
Here is an example of argoCD app descriptor:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: app-q-order-ms
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "300"
labels:
gitops.tier.layer: applications
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
spec:
destination:
namespace: openshift-gitops
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: applications
source:
path: quarkus-order-ms/config/dev
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
On the application tile, we can use the 'SYNC' to deploy the application or use argocd app sync <appname>.
ArgoCD app of app¶
The concept is to use a bootstrap application that will start other apps from gitops repository. (See video presentation here)
Connect pipeline to deployment¶
Once the manifests for a given app are defined in the gitops repository, we need to have the pipeline being able to update the deployment descriptor with the image reference and tag defined as part of the build pipeline.
The pipeline needs to have the git credentials to be able to write to the gitops repository. Credentials are saved in a secret and a configmap define github host, user.